[Java 기초문법] by Professional Java Developer Career Starter: Java Foundations @ Udemy
In general, generics allow us to kind of constrain what types of data we can associate with a class. We can use generics on methods and things that return data types as well. And also they can protect us from certain types of runtime errors because if you're not using generics, but you're working with code that is expecting to work with certain data types.
Respository class 생성
package datastore;
public class Repository {
}
records holders 생성
private List<String> records = new ArrayList<>();
repository pattern
very common name
List<String> findAll(){
return records;
}main method with actual action regarding repository
String findByID(long id){
return records.get(Long.valueOf(id).intValue());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Repository repo = new Repository();
repo.save("house");
repo.save("car");
}
이때 list generic보다 한단계 더 generic 타입을 사용하는 방법으로서 T를 사용할 수 있는데 이로써 데이터 타입을 지정해주지 않고 자유도를 높일 수 있다.
package datastore;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Repository<T> {
private List<T> records = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> findAll(){
return records;
}
T save(T record){
records.add(record);
return record;
}
T findByID(long id){
return records.get(Long.valueOf(id).intValue());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Repository repo = new Repository();
repo.save("house");
repo.save("car");
}
}
Here even though main method is not modified with type T right down there, it is allowed to instatntiate it still without any generic mentioning anywhere here.
Let's make another repo calss of a person.

with this can create another instance of a repository now, but this one will work for person instances and call it pRepo.
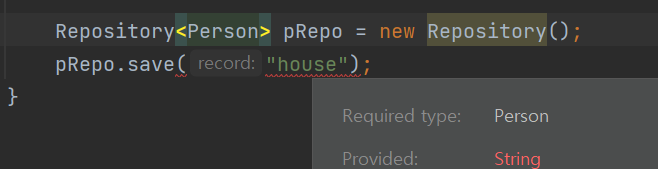
Repository<Person> pRepo = new Repository();
pRepo.save("house");
and here if I try to save string, occurs error saying that required type is Person.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Repository<String> repo = new Repository();
repo.save("house");
repo.save("boat");
Repository<Person> pRepo = new Repository();
pRepo.save(new Person("Jake", "Johnson"));
pRepo.save(new Person("Mary", "Johnson"));
pRepo.save(new Person("Jerry", "Johnson"));
System.out.println(pRepo.findAll());
}return :

That we didn't really have to change the underlying class of repo other than to just make it generic.
'Programming > Java, Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Java 기초문법] Collections, Set, Hashset, Treeset, List, Map (0) | 2022.10.21 |
|---|---|
| [Java 기초문법] 문자열 비교하기 , 필드, 메소드, 변수의 scope와 static, 열거형 (enum) (0) | 2022.10.21 |
| [Java 기초문법] Exceptions 자바 예외 처리 (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| [Java 기초문법] Streams API | Streams, stream의 다양한 메소드, sum, sort, filter (0) | 2022.10.20 |
| [Java 기초문법] collections, list, linked list, looping with iterators (0) | 2022.10.20 |



