스프링부트 자바 기반 웹개발 day 3
배열 구조 구현하기
불변 배열
package day3;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class ControllerStep1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// 추가 : 중복 값 존재하면 삽입 불가
// 추가 : 중복 값 전체 삭제
int[] arr = {10, 30, 40, 0, 0};
int[] arr2 = {10, 10, 20, 30, 40};
int[] arr3 = {10, 10, 20, 30, 30};
int cnt = getCountCurrentArray(arr);
deleteAsValue(10, arr2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr2));
// delAllDuplicate(arr2);
boolean run = true;
while (run) {
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[1]추가");
System.out.println("[2]삭제(인덱스)");
System.out.println("[3]삭제(값)");
System.out.println("[4]삽입");
System.out.println("[5]중복 전체 삭제");
System.out.println("[6]종료");
System.out.print("메뉴 선택 : ");
int command = scan.nextInt();
if (command == 1) {
System.out.print("추가할 값 입력 : ");
int data = scan.nextInt();
if (isDuplicate(data, arr)) {
System.out.println("중복 값이 존재합니다!");
return;
}
if (getCountCurrentArray(arr) >= arr.length) {
System.out.println("full!");
return;
}
arr[getCountCurrentArray(arr)] = data;
System.out.printf("%d 번째 %d 삽입 완료!\n", getCountCurrentArray(arr) + 1, data);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 2) {
System.out.print("삭제 인덱스 입력 : ");
int delIdx = scan.nextInt();
if ( isIndexEmpty(arr) || isArrayIndexOutOfRange(delIdx, arr) ) {
return;
}
IntStream.range(delIdx, getCountCurrentArray(arr)).forEach(v -> {
Runnable delIndexFunction = delIdx == 4 ? () -> arr[4] = 0 : () -> arr[v] = arr[v + 1];
delIndexFunction.run();
});
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 3) {
System.out.print("삭제 값 입력 : ");
int delVal = scan.nextInt();
if ( isIndexEmpty(arr) || !isValueExist(delVal, arr) ) {
return;
}
deleteAsValue(delVal, arr);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 4) {
System.out.print("삽입 인덱스 입력 : ");
int index = scan.nextInt();
if(isArrayIndexOutOfRange(index, arr)){
return;
}
System.out.print("삽입 값 입력 : ");
int data = scan.nextInt();
insert(arr, index, data);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 5) {
delAllDuplicate(arr2);
break;
} else if (command == 6){
break;
} else {
System.out.print("입력 오류");
}
}
}
private static void insert(int[] arr, int index, int data) {
for (int i = getCountCurrentArray(arr) - 1; i >= index; i--) {
arr[i + 1] = arr[i];
}
arr[index] = data;
}
private static void deleteAsValue(int delVal, int[] arr) {
IntStream.range(0, arr.length).forEach(v -> {
Runnable delFunction = arr[v] == delVal ? () -> {
IntStream.range(v, getCountCurrentArray(arr)).forEach(i -> arr[i] = arr[i + 1]);
} : () -> System.out.printf("%d번째 pass!\n", v);
delFunction.run();
});
}
private static int getCountCurrentArray(int[] array) {
return (int) Arrays.stream(array).filter(v -> v != 0).count();
}
private static boolean isIndexEmpty(int[] array) {
if (getCountCurrentArray(array) == 0) {
System.out.println("배열이 비어있습니다!");
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean isValueExist(int request, int[] array){
if (Arrays.stream(array).noneMatch(v->v==request)){
System.out.println("값이 존재하지 않습니다!");
return false;
}
return true;
}
private static boolean isArrayIndexOutOfRange(int request, int[] array) {
if (request >= getCountCurrentArray(array) || request < 0) {
System.out.println("배열 범위 바깥의 범위를 입력했습니다");
return true;
}
System.out.println("index 정상 입력!");
return false;
}
private static void showCurrentArray(int[] arr) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
private static boolean isDuplicate(int valueRequested, int[] array) {
return Arrays.stream(array).anyMatch(v -> v == valueRequested);
}
private static void delAllDuplicate(int[] array) {
/**
* TODO : 나중에 다시......
*/
// IntStream.range(0, getCountCurrentArray(array)).filter(v->array[v] == )
// int[] arr2 = {10, 10, 20, 30, 40};
// Arrays.stream(array).forEach(value -> {
// Runnable delAllFunction = isDuplicate(value, array) ? () -> deleteAsValue(value, array) : () -> System.out.printf("%s pass!\n", value);
// delAllFunction.run();
// });
// Arrays.stream(array).filter(v->isDuplicate(v,array))
// .forEach(v->{
//
// IntStream.range(0, getCountCurrentArray(array)).filter(i->array[i]==v).forEach(k->{
// array[k] = array[k + 1];
// });
// });
}
}
가변 배열
package day3;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
public class ControllerStep2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// 추가 : 중복 값 존재하면 삽입 불가
// 추가 : 중복 값 전체 삭제
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40};
// int[] arr = null;
boolean run = true;
while (run) {
showCurrentArray(arr);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("[1]추가");
System.out.println("[2]삭제(인덱스)");
System.out.println("[3]삭제(값)");
System.out.println("[4]삽입");
System.out.println("[5]중복 전체 삭제");
System.out.println("[6]종료");
System.out.print("메뉴 선택 : ");
int command = scan.nextInt();
if (command == 1) {
System.out.print("추가할 값 입력 : ");
int data = scan.nextInt();
arr = deepCopy(arr, data);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 2) {
if (isNullOrEmpty(arr)) {
System.out.println("null or empty");
return;
}
System.out.print("삭제 인덱스 입력 : ");
int delIdx = scan.nextInt();
arr = delAsIndex(arr, delIdx);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 3) {
if (isNullOrEmpty(arr)) {
System.out.println("null or empty");
return;
}
System.out.print("삭제 값 입력 : ");
int delVal = scan.nextInt();
arr = delAsValue(arr, delVal);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 4) {
System.out.print("삽입 인덱스 입력 : ");
int index = scan.nextInt();
System.out.print("삽입 값 입력 : ");
int data = scan.nextInt();
arr = deepCopy(arr, data, index);
showCurrentArray(arr);
} else if (command == 5) {
break;
} else if (command == 6) {
break;
} else {
System.out.print("입력 오류");
}
}
}
private static boolean isNullOrEmpty(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null) {
System.out.println("null !!! ");
return true;
}
if (arr.length == 0) {
System.out.println("empty !!!");
return true;
}
return false;
}
private static int[] deepCopy(int[] source) {
source = handleNullWithAddFunction(source);
int[] temp = source;
source = new int[temp.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
source[i] = temp[i];
}
source[source.length - 1] = 0;
return source;
}
private static int[] deepCopy(int[] source, int valueToBeAdded) {
source = handleNullWithAddFunction(source);
int[] temp = source;
source = new int[temp.length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
source[i] = temp[i];
}
source[source.length - 1] = valueToBeAdded;
return source;
}
private static int[] deepCopy(int[] source, int valueToBeAdded, int index) {
source = insert(deepCopy(source), valueToBeAdded, index);
return source;
}
private static int[] insert(int[] source, int valueToBeAdded, int index) {
for (int i = getCountCurrentArray(source) - 1; i >= index; i--) {
source[i + 1] = source[i];
}
source[index] = valueToBeAdded;
return source;
}
private static int[] delAsIndex(int[] source, int indexToBeDeleted) {
int[] temp = source;
source = new int[temp.length - 1];
for (int i = indexToBeDeleted; i < temp.length - 1; i++) {
source[i] = temp[i + 1];
}
return source;
}
private static int[] delAsValue(int[] source, int valueToBeDeleted) {
int[] temp = source;
int[] newSource = new int[temp.length - 1];
Arrays.stream(temp).filter(v -> v == valueToBeDeleted).forEach(v -> {
IntStream.rangeClosed(0, getIndex(valueToBeDeleted, source)).forEach(i -> newSource[i] = temp[i]);
IntStream.range(getIndex(valueToBeDeleted, source), newSource.length).forEach(
i -> newSource[i] = temp[i + 1]);
});
return newSource;
}
private static int[] handleNullWithAddFunction(int[] array) {
return Arrays.stream(array != null ? array : new int[0]).toArray();
}
private static int getCountCurrentArray(int[] array) {
return (int) Arrays.stream(array != null ? array : new int[0]).filter(v -> v != 0).count();
}
private static void showCurrentArray(int[] source) {
if (source == null) {
System.out.println("null !");
return;
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(source));
}
private static int getIndex(int value, int[] arr) {
return IntStream.range(0, arr.length).filter(i -> arr[i] == value).findFirst().getAsInt();
}
}
클래스의 존재이유
- > 배열에는 한가지 자료형 밖에 들어간다는 특징 !
=> 그 한계를 극복하기 위함이다.
=> 클래스 : 사용자 정의 자료형 !
클래스는 일종의 설계도 : 미리 방을 만들지 않는다.
class Member {
//멤버변수(인스턴스 변수, 스태틱 변수), 필드
// new 할 때 heap 메모리 방에서 생성 : with 주소값 + 자동 초기값
String id;
int pw;
String name;
}
저장 되는 방식은 배열과 동일하다
주소 = 실제로는 해쉬코드
컴퓨터의 실제 메모리는 계속 바뀐다. jvm이 돌아가는 동안 유지해주기 위해 해쉬코드를 별도로 생성해서 주소값으로 사용한다.
배열은 인덱스로 접근
클래스는 .으로 접근
자료구조형의 stack, heap => 구현된 자료구조랑 개념적으로의 차이
jvm에서 사용하는 스택 => 엄밀히는 call stack이라고 부른다. 추상적으로 먼저 정의된 stack을 특성을 사용하였기에 call stack이라고 하게 되었음
메모리 구조를 연습해보자
package day3.practiceArray;
public class ClassMemoryPractice {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample01 s1 = new Sample01();
int num = 50;
s1 = new Sample01();
s1.a = 10;
s1 = null;
s1 = new Sample01();
s1.b = num;
}
}
지역 변수 = 2개

package day3;
class Sample02 {
int[] list;
int num;
int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
}
public class ClassMemoryPractice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Sample02 s4 = new Sample02();
Sample02 temp = s4;
s4 = null;
s4.arr = arr;
}
}

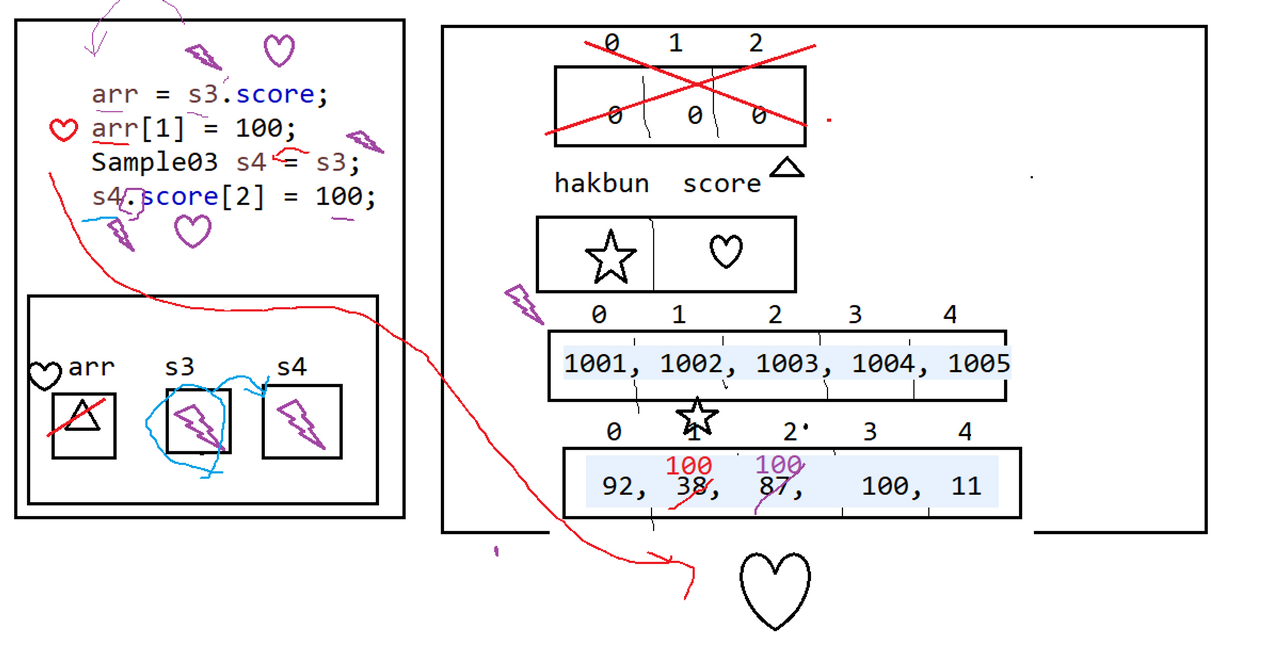
package day3;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Sample03 {
int[] hakbun = { 1001, 1002, 1003, 1004, 1005 };
int[] score = { 92, 38, 87, 100, 11 };
}
public class ClassMemoryPractice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[3];
// 변수의 생성 => 변수 선언 + 변수 초기값 할당
Sample03 s3; // 변수 선언
s3 = new Sample03(); // 초기값 할당
arr = s3.score;
arr[1] = 100;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s3.score));
Sample03 s4 = s3;
s4.score[2] = 100;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s4.score));
}
}
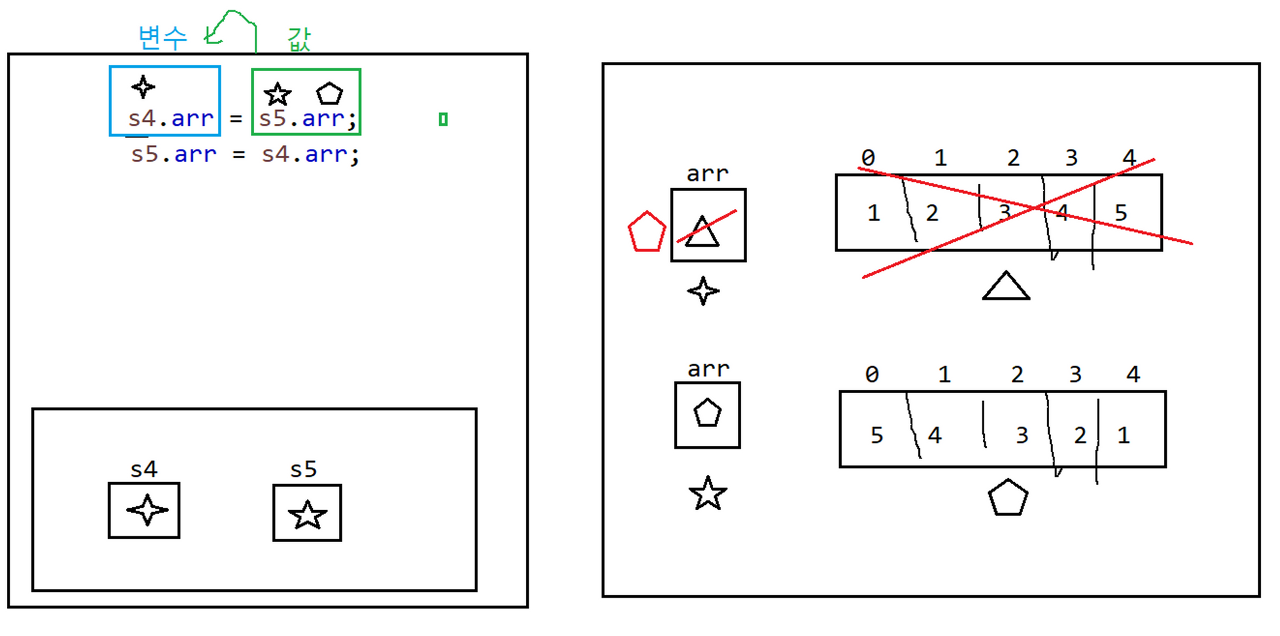
package day3;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Sample04 {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
}
class Sample05 {
int[] arr = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
}
public class ClassMemoryPractice4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sample04 s4 = new Sample04();
Sample05 s5 = new Sample05();
s4.arr = s5.arr;
s5.arr = s4.arr;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s4.arr));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s5.arr));
// 두 개 배열을 교체해보자 ! => 5 4 3 2 1 <=> 1 2 3 4 5
s4.arr = convert2(s5.arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s4.arr));
arrayConversion(s4, s5);
}
private static void arrayConversion(Sample04 s4, Sample05 s5) {
int[] temp = s5.arr;
s5.arr = s4.arr;
s4.arr = temp;
}
private static int[] convert1(int[] array) {
int[] newArray = new int[array.length];
int count = 0;
for (int i = array.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
newArray[i] = array[count];
count++;
}
return newArray;
}
private static int[] convert2(int[] array) {
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
temp = array[array.length - 1-i];
array[array.length - 1 - i] = array[i];
array[i] = temp;
}
return array;
}
}
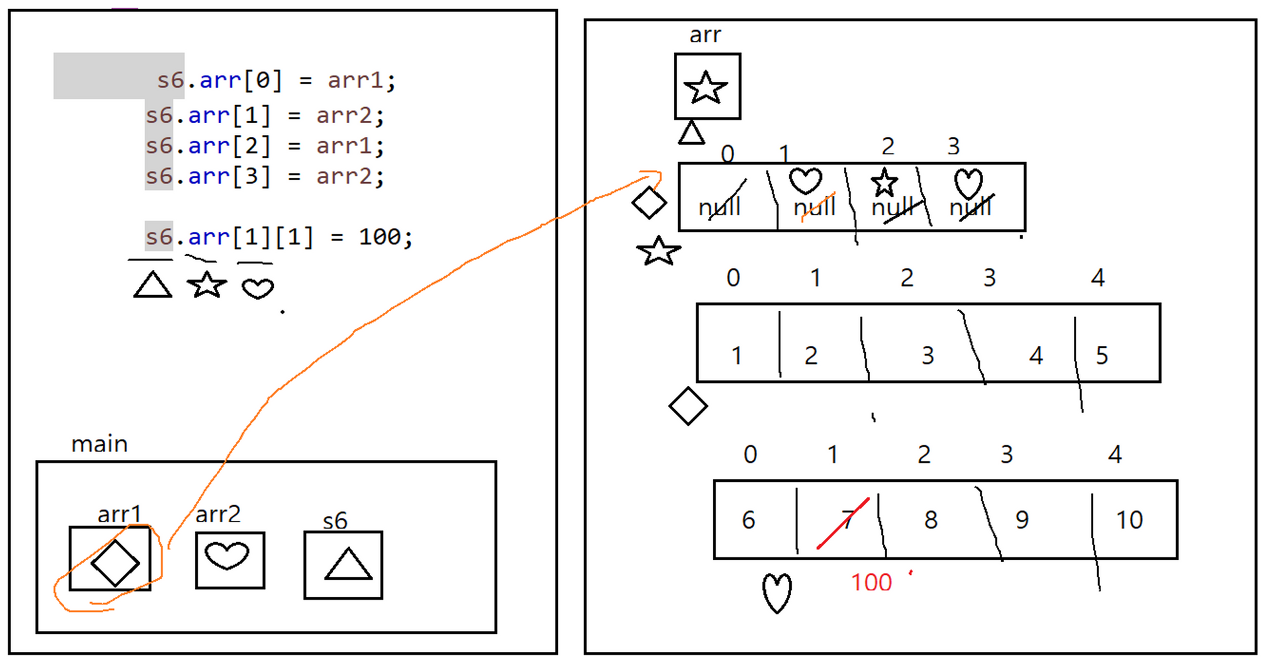
package day3;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Sample06 {
int[][] arr = new int[4][];
}
public class ClassMemoryPractice5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] arr2 = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
Sample06 s6 = new Sample06();
s6.arr[0] = arr1;
s6.arr[1] = arr2;
s6.arr[2] = arr1;
s6.arr[3] = arr2;
s6.arr[1][1] = 100;
for(int i=0; i<s6.arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s6.arr[i]));
}
}
}
Omr 문제를 풀어보자
package day3.quizOMR;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
class Ex06 {
int[] answer = {1, 3, 4, 2, 5}; // 시험답안
int[] hgd = new int[5]; // 학생답안
int cnt = 0; // 정답 맞춘 개수
int score = 0; // 성적
}
public class QuizOmr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* # OMR카드 : 클래스 + 변수
* 1. 배열 answer는 시험문제의 정답지이다.
* 2. 배열 hgd에 1~5 사이의 랜덤 숫자 5개를 저장한다.
* 3. answer와 hgd 값을 비교해 정오표를 출력한다.
* 4. 한 문제당 20점이다.
* 예)
* answer = {1, 3, 4, 2, 5}
* hgd = {1, 1, 4, 4, 3}
* 정오표 = {O, X, O, X, X}
* 성적 = 40점
*/
Ex06 ex06 = new Ex06();
IntStream.range(0, ex06.hgd.length).forEach(i->ex06.hgd[i] = getRandom());
String[] answerSheet = new String[ex06.hgd.length];
IntStream.range(0, ex06.hgd.length).forEach(i->{
Runnable drawFunction = ex06.answer[i] == ex06.hgd[i] ? ()-> {answerSheet[i]="O"; ex06.cnt++;} :()-> answerSheet[i]="X";
drawFunction.run();
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ex06.answer));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ex06.hgd));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(answerSheet));
System.out.printf("count: %s\n", ex06.cnt);
System.out.printf("score: %s점", ex06.score = ex06.cnt * 20);
}
private static int getRandom(){
Random random = new Random();
return random.nextInt(1,6);
}
}
반응형
'교육 > Java&Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| kosta 클라우드 네이티브 애플리케이션 개발 과정 day 21 (docker) (0) | 2023.01.17 |
|---|---|
| kosta 클라우드 네이티브 애플리케이션 개발 과정 day 20 (0) | 2023.01.16 |
| kosta 클라우드 네이티브 애플리케이션 개발 과정 day 19 (0) | 2023.01.13 |
| kosta 클라우드 네이티브 애플리케이션 개발 과정 day 18 (0) | 2023.01.13 |
| kosta 클라우드 네이티브 애플리케이션 개발 과정 day 17 (2) | 2023.01.11 |



